What is Business Email Compromise (BEC)?
Business Email Compromise involves impersonating an employee, manager or business partner in order to get the recipient to perform certain actions.
BEC is always about manipulating employees of companies or institutions via email. The aim is either to transfer money to the fraudsters’ accounts or to pass on sensitive data and confidential information to them. Affected companies can be found in all sectors: in 2016, the car supplier Leoni (damage: 40 million euros) and the company Ubiquiti Networks (damage: 46.7 million dollars) were hit, in 2017, Dublin Zoo.
These are just three examples from a seemingly endless number of successful attacks with Business Email Compromise, and they show that the financial damage can be immense: The FBI recorded $26 billion in losses in the US and abroad related to BEC attacks between June 2016 and July 2019.
What is the difference between Business Email Compromise and CEO Fraud?
CXO Fraud, CEO Fraud, Fake President Fraud (FPF), BEC – all these terms describe the use of false identities as the basis for a fraud scheme. However, these terms are not entirely congruent, because BEC – as the name suggests – is based on attacks via email, while all the other methods also allow for other contact channels, such as deep-fake telephone calls.
Another difference is the fact that with BEC, the criminals do not always pose as a higher-ranking person; the identities of other people who have some kind of relationship to the affected company are also faked. These can be employees of their own company, but also customers, partners, lawyers, consultants or the like.
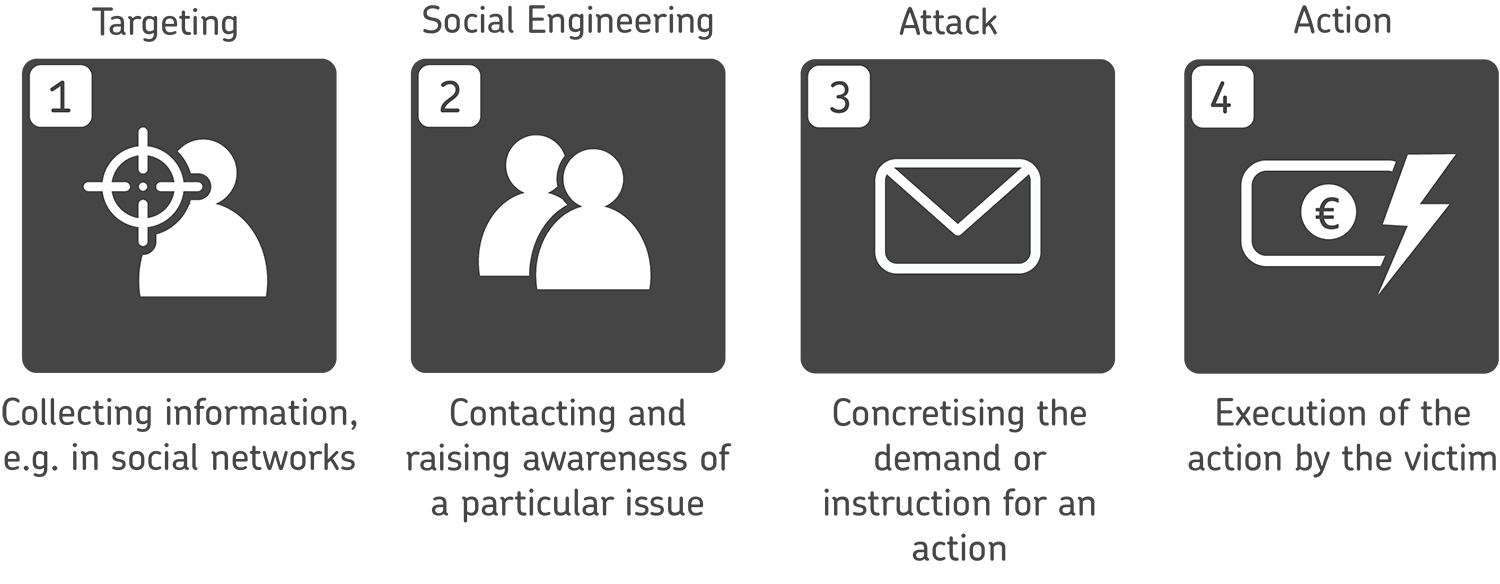
BEC attacks are well prepared
The fake emails are indistinguishable from real emails for the untrained – and sometimes even for the trained – viewer. They appear completely authentic, are written in grammatically correct language and are elaborately designed, including company logo and email disclaimer.
This is possible because the victims are spied on beforehand by means of social engineering and spear phishing and then targeted. The typical characteristics of phishing emails are therefore increasingly no longer useful as indicators of phishing emails as the quality of the attacks increases, because the technical possibilities of the criminals are also developing rapidly.
The preparation of a BEC attack therefore mainly consists of obtaining information about the subsequent victim. In this way, the criminals try to find out details about the company itself, employees, supervisors, processes, current events and other company internals. The more information the criminals can obtain, the higher the probability that the attack will be successful.
Spying is only the first step
Spying is in many cases first carried out via social networks in order to identify later victims. Sometimes contact is then made by phone or email to “sensitise” employees to the facts, i.e. to prevent doubts from arising later.
So-called spoofing is often used in this process: Using falsified email addresses, the attackers insert themselves into existing communication flows and collect further information, for example, about a certain process that could involve a major financial transaction. As soon as the “right” contact person has been found and the time seems appropriate, the attack is carried out. This means: The supposedly known communication partner instructs the victim, for example, to make a transfer to another account or to send or release a certain file.
Typical characteristics of Business Email Compromise (BEC)
It is not uncommon for some form of psychological pressure to be exerted. The following characteristics are typical for Business Email Compromise:
How can you protect yourself from BEC?
Comprehensive employee awareness is the first step to preventing Business Email Compromise and protecting your business. This is especially fundamental because BEC attacks are becoming increasingly difficult to detect, the quality of fraudulent emails is getting higher and higher, and they are becoming more and more homogeneous in existing communication flows. Employees must be trained to recognise suspicious emails and to react to them accordingly. Under no circumstances should they reply to potentially dangerous emails.
In addition, the right email gateway also protects against BEC attacks by, for example, recognising keywords such as transfer, urgent, payment or secret and filtering out the corresponding emails.
Ideally, such a gateway also offers the possibility to compare sender names of inbound emails with the names of employees. Fake emails sent to victims in the name of superiors or employees are thus intercepted.
Reliable protection against BEC – with NoSpamProxy
The CxO fraud detection in NoSpamProxy compares the sender name of incoming emails with the names of crucial users in your company. In this way, fake emails sent to you or your employees in the name of superiors, employees or customers are intercepted.
90 per cent of all cyber attacks occur via email. A reliable email security solution is the surest protection against malware, ransomware and spam. And against rash transfers to cyber criminals.