What is TLS encryption?
TLS stands for Transport Layer Security, which roughly translates to transport layer security. It is an encryption protocol that is mainly used with HTTPS. The term “transport layer” here means the corresponding layer in the TCP/IP model. The TCP protocol ultimately enables communication between two devices. In short, TLS ensures that content can be transmitted encrypted on the internet.
Thus, TLS is the basis for the encryption of communication between web applications and servers, for example web browsers (see above, HTTPS). It is important to mention that TLS is also crucial for the secure transmission of emails and other communication. For example, TLS is used to encrypt POP3 (as POP3S), IMAP (as IMAPS), SMTP (as SMTPS) and FTP (as FTPS), among others.
How does TLS encryption work?
With TLS, we speak of hybrid encryption, i.e. a mixture of asymmetric and symmetric encryption.
As soon as a client – let’s say a web browser – contacts the web server, this web server sends its certificate to the client. This certificate proves the authenticity of the server. The basic prerequisite is therefore that a TLS certificate is installed on the server.
This initiation of a TLS connection is called a TLS handshake. During the TLS handshake, client and server connect.
The client checks the certificate and sends the server a random number encrypted with the server’s public key. The server uses this random number to generate the session key with which the communication is to be encrypted. Since the random number comes from the client, the client can be sure that the session key actually comes from the server. The server then sends the encrypted session key to the client.
Why is hybrid encryption used with TLS? The answer: speed. If the data were also secured by means of asymmetric encryption, the entire communication would slow down considerably.
Why is transport encryption important?
The use of TLS has three goals:
The importance of transport encryption through TLS can also be justified with the help of the requirements of the GDPR. For example, the State Commissioner for Data Protection and Freedom of Information in North Rhine-Westphalia points out that responsible parties who send email messages containing personal data must ensure mandatory transport encryption. However, it should also be mentioned that the use of TLS is only the minimum requirement and STARTTLS (see below) cannot replace email encryption using S/MIME or PGP.
What is the difference between SSL and TLS?
TLS is based on Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), which was developed by Netscape and introduced in 1995. TLS version 1.0 was released in 1999 and was planned as version 3.1 of SSL. However, it was then introduced as an improved version of SSL 3.0 and previously renamed TLS.
The difference between SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0 is negligible. Version TLS 1.2 then brought significantly improved security as well as greater flexibility in terms of the encryption used (cipher suites).
The current TLS version is 1.3. Since the term SSL is still very common, it is often used synonymously with TLS, or a double designation such as SSL/TLS is used.
Setting up TLS encryption in NoSpamProxy
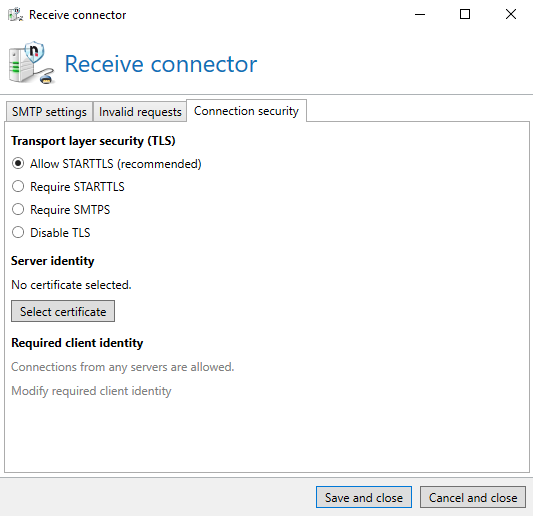
Setting up TLS encryption in NoSpamProxy is easy. All you have to do is store a valid TLS certificate on the Gateway Role and then select it in the SMTP receive connectors as well as in the outbound send connectors.
STARTTLS is an additional command within the SMTP protocol. The connection establishment from the sending host to the receiving host is unencrypted. Thus, the initial EHLO command is sent, as is the response from the receiving server. In this response, the recipient signals that it supports STARTTLS and the sending server can decide for itself whether to accept the offer or not.
With SMTP, on the other hand, the connection is encrypted from the first moment. The reason for using STARTTLS is to avoid possible compatibility problems.
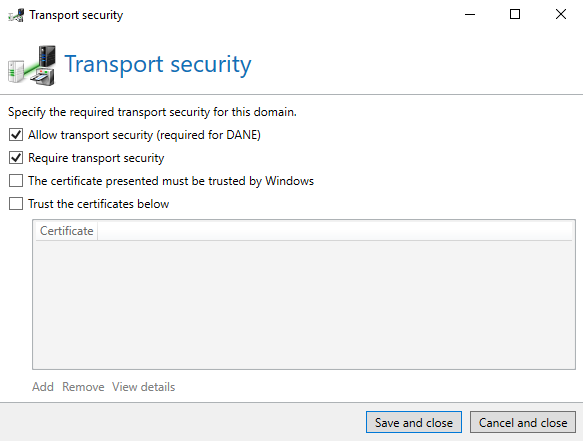
In the partner settings, you can also enforce transport security through TLS individually for each partner and even store the certificate that the partner must use for communication.
Not yet using email encryption?
Encrypting emails is secure with NoSpamProxy Encryption – and very easy! Ensure legally compliant and GDPR-compliant email communication now. Test NoSpamProxy now for 30 days free of charge.